Storage Products: 3 Ways to Create Value in the Circular Economy
Introduction
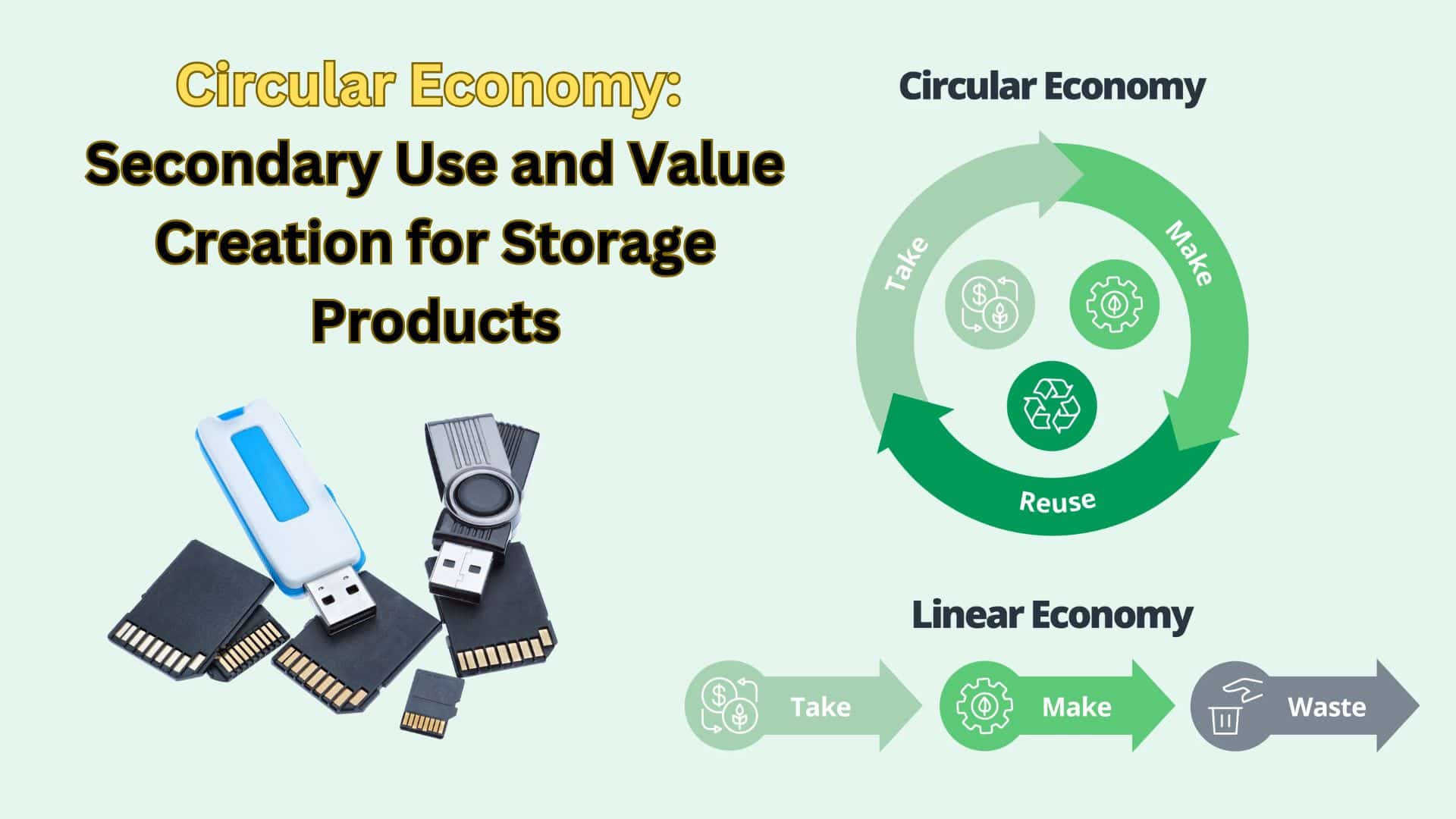
The concept of the circular economy has become increasingly important across various industries, including the storage sector, as businesses and consumers look for sustainable alternatives to the traditional “take, make, dispose” model. In this context, the idea of reusing, repurposing, and recycling storage products such as memory cards and external hard drives has gained significant attention. This article explores the potential of creating value through the secondary use of storage products, focusing on how companies and individuals can participate in a more sustainable, circular system.
What is a Circular Economy?
- Definition of the Circular Economy and How It Contrasts with the Traditional Linear Economy
The circular economy refers to an economic model that prioritizes the continual use of resources through repair, reuse, refurbishment, and recycling. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a “take, make, dispose” approach, the circular economy aims to extend the life cycle of products, reducing waste and the demand for raw materials. In the storage industry, this means not only designing products with longevity in mind but also ensuring that they can be easily repurposed or recycled at the end of their life cycle.
- The Role of Storage Products in the Circular Economy
Storage products such as solid-state drives (SSDs), memory cards, and external hard drives have a significant role to play in the circular economy. These devices, like other electronics, have a finite life span but contain valuable components that can be reused or repurposed. By shifting toward a circular model, storage products can be designed with sustainability in mind, minimizing waste and reducing the need for new materials.
Extending the Life Cycle of Storage Products
- How Businesses and Consumers Can Reuse and Repurpose Old Storage Devices
One of the primary goals of the circular economy is to extend the useful life of products. Old storage devices can often be reused for secondary purposes, preventing them from ending up in landfills. Businesses and consumers can repurpose old storage devices in various ways, such as:
- Using outdated memory cards for archival purposes or as backup storage for personal files.
- Repurposing external hard drives for other technological applications or as media storage for offices or creative industries.
- Using storage devices in DIY tech projects or educational kits for tech enthusiasts and schools.
- Examples of Secondary Use for Storage Products
- Repurposing Memory Cards for Industrial Applications: Memory cards, especially those designed for cameras or smartphones, can be repurposed for use in industrial settings. For example, companies may use old memory cards in automation or machinery where the need for fast data storage isn’t as critical.
- Refurbishing External Hard Drives for Personal or Business Use: External hard drives that no longer meet high-performance standards can still be used for non-critical tasks like document storage, backup services, or distributing media in environments with less intensive storage needs.
By embracing these secondary uses, businesses and consumers contribute to the sustainability efforts of the circular economy.
Refurbishment and Recycling Programs
- Benefits of Refurbishment and Recycling for Storage Devices
Refurbishment and recycling programs are key components of the circular economy, helping to reduce waste and extract value from old products. These programs not only reduce the environmental impact of discarded storage products but also help recover valuable materials such as metals, plastics, and rare earth elements. Refurbishing storage devices can also offer businesses a cost-effective alternative to purchasing new products.
- Environmental Benefits: By recycling and refurbishing storage devices, harmful electronic waste (e-waste) is reduced, conserving resources and preventing hazardous substances from leaching into the environment.
- Economic Benefits: Refurbishment programs can create value by extending the life of devices, providing affordable options for customers, and allowing businesses to sell or donate refurbished products.
- Industry Examples of Storage Product Take-Back Programs and Partnerships with Recycling Companies
Many businesses in the storage industry are recognizing the importance of taking responsibility for their products at the end of their life. For instance, companies like Western Digital and Seagate have implemented take-back programs that allow consumers to return old devices for recycling or refurbishment. These companies work with certified recycling partners to ensure that the storage products are properly dismantled and recycled in an environmentally friendly manner.
- Tech giants like Apple have also embraced the circular economy by offering trade-in programs, ensuring that used storage devices are either recycled or refurbished for resale.
Creating New Value from Old Products
- How Refurbished Storage Products Can Generate Value While Reducing Environmental Impact
Refurbishing storage products allows businesses to generate revenue while reducing their carbon footprint. For example, refurbished SSDs and hard drives can be sold at lower prices, making them more accessible to consumers who may not need the latest model but still require reliable storage. By investing in refurbishment programs, companies can also minimize the environmental impact associated with manufacturing new products.
- How Businesses Can Monetize Second-Hand Storage Devices or Contribute to Sustainability Initiatives
Storage products that are no longer in high demand can be sold or donated for secondary use. Businesses can set up online marketplaces to sell refurbished or second-hand storage devices. Additionally, these businesses can partner with non-profit organizations or educational institutions to donate old products, helping those in need while promoting a circular economy model.
Furthermore, by contributing to recycling initiatives or offering incentives for customers to return old products, companies can engage in sustainability efforts that enhance their corporate social responsibility profile.
Conclusion
Incorporating the principles of the circular economy into the storage industry offers numerous benefits for businesses, consumers, and the planet. From extending the life cycle of storage products to refurbishing and recycling old devices, every step helps to reduce waste and create new value from existing resources. By embracing secondary use, refurbishment programs, and recycling initiatives, companies can participate in a global movement towards more sustainable and eco-conscious practices. Businesses should encourage consumers to consider the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions and support initiatives that promote the circular economy.